What Are The Core Principles Of Student-Centered Learning?
by TeachThought Staff
Like any phrase, ‘student-centered learning’ is subjective and only useful insofar as it ultimately supports the design of learning experiences for students.
For example, arguing for a ‘student-centered approach’ to creating curriculum frameworks that center the authentic knowledge needs of each student makes sense, while creating a ‘student-centered’ classroom that gives students little choice in content, voice in product, or a human necessity for creative expression does not. Student-centeredness uses an actual person as an audience, and designs learning experiences backwards from that point.
With that in mind, here are four (of countless) principles of student-centered learning to consider as you design curriculum and instruction.
4 Principles Of Student-Centered Learning
A Definition of Student-Centered Learning
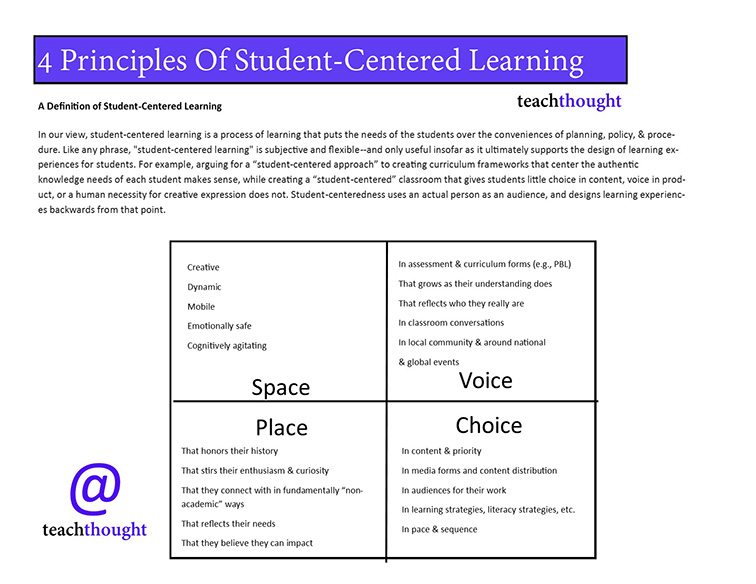
In our view, student-centered learning is a process of learning that puts the needs of the students over the conveniences of planning, policy, and procedure. We can consider how to center students according to four categories: space (where and how students are learning); place (not necessarily a physical location, but a moment in time and culture and reinforced by context and history); voice (emerging through individual reflection and collaborative discussion); and choice (agency in how they learn, at what rate, and what depth).
Space
Creative
Dynamic
Mobile
Emotionally safe
Cognitively agitating
Place
That honors their history
That stirs their enthusiasm and curiosity (using strategies that cause curiosity)
That they connect with in fundamentally “non-academic” ways
That reflects their needs
That they believe they can impact
Voice
In assessment & curriculum forms (e.g., PBL)
That grows as their understanding does
That reflects who they really are
In classroom conversations
In local, national, and global events
Choice
In content & priority
In media forms and content distribution
In audiences for their work
In learning strategies, literacy strategies, etc.
In pace & sequence
4 Principles Of Student Centered Learning