by TeachThought Staff
For a growing child, grade level seems to have very little use.
For a child functioning as or in the role of a ‘student,’ it can be vaguely useful to schools to place students and stratify them in what is expected to be similar ability levels, ages, and in the best case, maturity, and social skills.
The History Of Age-Based Grade Levels In The United States
The history of age-based grade levels in the United States can be traced back to the early 19th century when the American education system was formalized and standardized. Before this, education was often provided in one-room schoolhouses, and students of various ages and abilities were taught together. However, as the country began to urbanize and industrialize, there was a growing need for a more structured and organized education system.
Horace Mann, often called the “father of American public education,” significantly shaped the age-based grade-level system. In the mid-19th century, he advocated for establishing graded schools, where students would be grouped by age and academic ability into specific grade levels.
This system aimed to provide a more uniform and efficient education, ensuring students progressed through a standardized curriculum at an appropriate pace for their age. Over time, this model became the foundation of the modern American education system, with students advancing from kindergarten through 12th grade based on age, typically starting kindergarten around age 5 and completing high school by the age of 18.
Today, the age-based grade level system remains the standard in the United States. However, ongoing debate and reform efforts have been to address educational equity, individualized learning, and the recognition of diverse student needs and abilities within this framework.
See also The Pros And Cons Of Using Grade Levels In School
Understanding how ages correspond to learning levels is important for successful educational planning and adaptation of learning materials. Students often need to select essay topics that match their knowledge and interests. In such cases, Essay Idea Generator by Textero helps, quickly suggesting suitable ideas and facilitating the selection process. This tool is especially useful when students want to develop their thoughts by choosing relevant and interesting topics for their papers.
Note that the following answer to ‘What are the grade levels in Elementary, Middle, and High School?” depends on where you live. What grade should a 10-year-old be in? How old should a 1st-grader be?
In many countries, the labeling is altogether different. In the UK, for example, ‘grades’ might be called ‘years’ as in Year 1, Year 2, and so on. So, the following list of ages by grade levels is based on the United States but should roughly apply to the formal education system for most countries.
It also depends on what age the student actually enters kindergarten, where their birthday falls in relation to the school calendar, and if they’ve failed a grade or been ‘held back’ or skipped forward in grade levels.
Within that context, here are–in most cases–the ages by grade level.
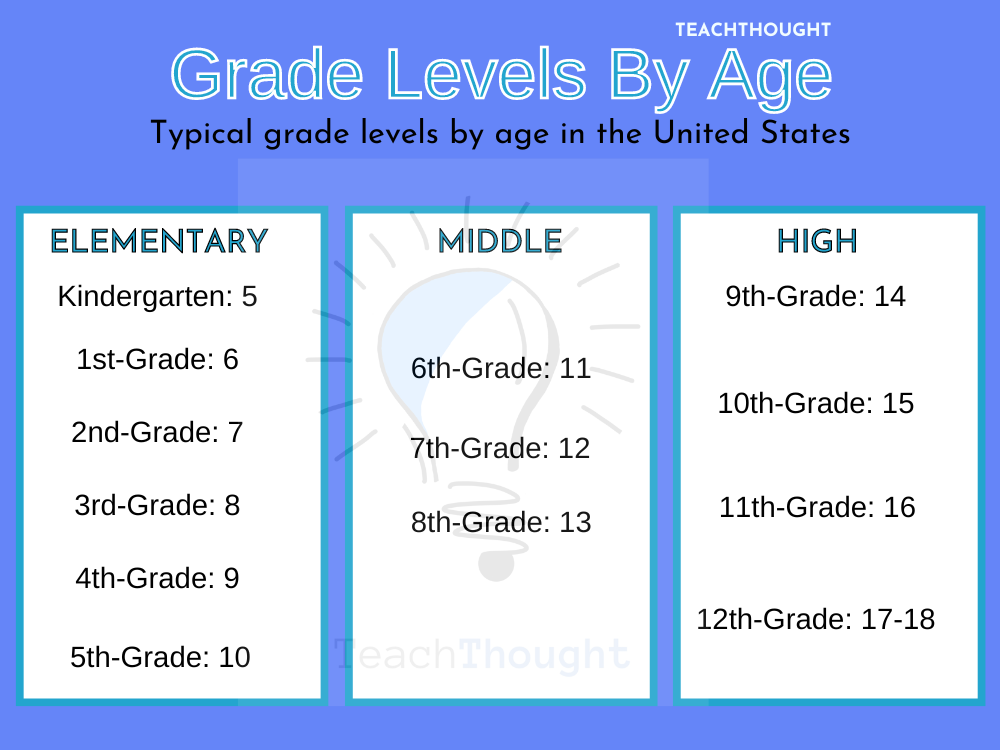
What Are The Grade Levels By Age?
Pre-School
Pre-K2: 2
Pre-K3: 3
Pre-K4: 4
Elementary School Grade Levels By Age
Kindergarten: 5
1st-Grade: 6
2nd-Grade: 7
3rd-Grade: 8
4th-Grade: 9
5th-Grade: 10
Middle School Grade Levels By Age
6th-Grade: 11
7th-Grade: 12
8th-Grade: 13
See also Commonly Misspelled Words
High School Grade Levels By Age
9th-Grade: 14
10th-Grade: 15
11th-Grade: 16
12-Grade: 17-18
See also 10 Tips For Teaching Mindfulness In School At Any Grade Level
