ASSIStive Technology
A Quick Overview Of Assistive Technology Aids
Assistive technology refers to any device, equipment, software, or system that is designed to assist individuals with disabilities in performing tasks, improving their quality of life, and enhancing their overall independence.
Assistive technologies can compensate for limitations or disabilities and enable people to overcome barriers they may face in various aspects of life, such as communication, mobility, education, employment, and daily activities.
Assistive technology aids include visual aids, mobility aids, hearing aids, sip and puff systems, cognitive and learning aids.
Another strategy for using assistive technology in the classroom include using environmental control systems–devices enable individuals with physical disabilities to control various aspects of their environment, such as lighting, temperature, and appliances, using assistive switches or voice commands.
These technologies help individuals with visual impairments by magnifying text or images, converting written text into speech, or providing tactile feedback. Examples include screen readers, braille displays, and electronic magnifiers.
Cognitive and learning aid technologies support individuals with cognitive impairments or learning disabilities in organizing information, remembering tasks, and enhancing their learning experience. Examples include electronic organizers, specialized software, and apps for cognitive skills training.
Examples Of Assistive Technology Tools For Special Education?
What Is Assistive Technology?
Assistive technology refers to any device, equipment, software, or system that is designed to assist individuals with disabilities in performing tasks, improving their quality of life, and enhancing their overall independence in the classroom.
These technologies can compensate for limitations or disabilities and enable students to overcome barriers they may face in various aspects of life, such as communication, mobility, education, and daily activities for learning in the classroom and functions outside of the classroom.
See also How Technology Is Changing How Teachers Communicate With Students
What Are Some Examples of Assistive Technology For Learning In The Classroom?
What are some examples of assistive technology in the classroom for students with disabilities?
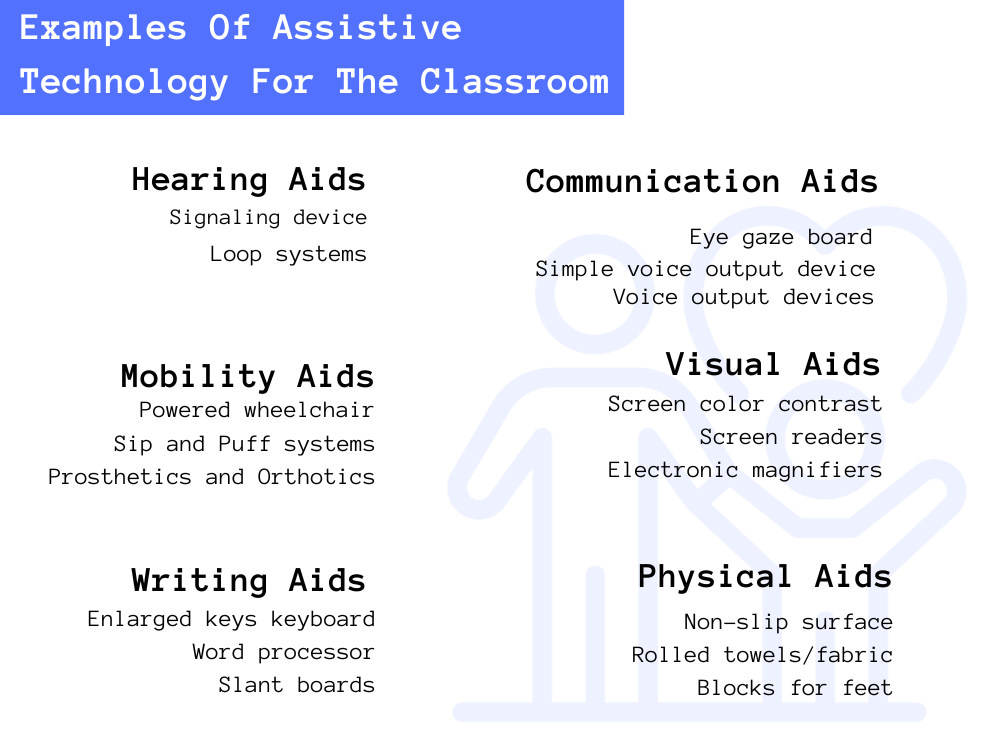
Mobility aids
While mobility aids depend on the disability of the student, examples can include wheelchairs, walkers, and prosthetic limbs, which help individuals with mobility impairments to move around independently.
Communication aids: These devices assist people with speech or communication difficulties expressing themselves. Examples include speech-generating devices, text-to-speech software, and augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) systems.
Other examples of mobility aids:
-Grab rails
-Powered wheelchair with joystick, head switch, or sip/puff control
-Other powered mobility toy
See also 15 Assistive Technology Tools & Resources For Students With Disabilities
Visual Aids
These technologies help individuals with visual impairments by magnifying text or images, converting written text into speech, or providing tactile feedback. Examples include screen readers, braille displays, and electronic magnifiers.
Other examples of vision/visual aids:
-Eyeglasses
-Magnifier CCTV Screen color contrast
-Enlarged keys keyboard
-Screen color contrast
-Braille translation software or printer
Hearing aids and assistive listening devices
These devices amplify sound and help students with either complete or partial hearing loss. These hearing aid assistive listening devices can include hearing aids, cochlear implants, and assistive listening systems.
Other examples of hearing/assistive listening aids:
-Pen and paper
-Word processor
-TTY/TDD for phone access
-Signaling device
-Closed captioning
-Device-aided note-taking
-Hearing aid
-Personal amplification system
-Loop system
-Infrared system
Cognitive and learning aids
Cognitive and learning aid technologies support individuals with cognitive impairments or learning disabilities in organizing information, remembering tasks, and enhancing their learning experience. Examples include electronic organizers, specialized software, and apps for cognitive skills training.
Writing mechanics aids can include adapted paper, slantboards, portable wordprocessors, and specialized pencils or pens with unique grips
Sip and Puff Systems
Sip and puff systems are assistive technology devices designed for individuals with limited mobility, typically those with severe physical disabilities. These systems detect the user’s inhalation (sip) and exhalation (puff) through a specialized sensor or switch.
Students control various functions, such as typing on a keyboard, moving a wheelchair, or interacting with a computer by sipping and puffing in specific patterns or sequences that are pre-programmed or customized according to their needs. The sensor translates these inhalation and exhalation actions into electrical signals, allowing the user to execute specific commands or tasks.
Utilizing the natural movements of breathing, sip and puff systems empower individuals with limited motor skills to access and control various devices and technologies, thereby enhancing their independence and facilitating their participation in daily activities.
Examples of Assistive Tools For Communication
Communication board/book with pictures, objects, letters, or words
Eye gaze board
Simple voice output device
Voice output device with icon sequencing (e.g., AlphaTalker, Liberator, and Chatbox)
Voice output device with dynamic display (e.g., Dynavox, Speaking Dynamically, etc.)
Devie with speech synthesis for typing (e.g., Cannon Communicator, Link, Write: OutLoud, etc.)
Environmental Control Systems
Another strategy for using assistive technology in the classroom includes using environmental control systems–devices enable individuals with physical disabilities to control various aspects of their environment, such as lighting, temperature, and appliances, using assistive switches or voice commands.
Prosthetics and Orthotics
These devices are used to replace or support missing or impaired body parts, such as limbs, joints, or braces, to enhance mobility and function.
Prosthetics and orthotics are valuable assistive devices that can significantly enhance the educational experience for students with physical disabilities in the classroom. Prosthetic limbs can enable students with limb loss or impairments to achieve greater mobility and independence, facilitating their ability to access educational materials and participate in physical activities alongside their peers.
Additionally, orthotic devices, such as braces or splints, can provide stability and support to students with musculoskeletal conditions, allowing them to sit comfortably, maintain proper posture, and engage in classroom activities with reduced discomfort or fatigue. By addressing mobility and physical challenges, prosthetics and orthotics contribute to a more inclusive and empowering learning environment, enabling students to focus on their education and social interactions.
Examples of Assistive Technology Aids For Physical Seating include non-slip surfaces, custom-fitted wheelchair or insert, bolsters, rolled towel, and blocks for feet.
